Velilla Group Regulations
EN ISO 13688
Protective clothing
This standard specifies general requirements for ergonomics, safety, sizing, ageing and labelling of protective clothing. It can only be used in conjunction with other standards.
EN 14058
Cold environments
Protection against the effects of cold environments between -5ºC and 10ºC.

- Y Heat resistance class
- Y Air permeability class (optional)
- Y Water penetration resistance class (optional)
- Y Insulation value, Icler in m2k/W (optional)
- Y Insulation value, Icle in m2k/W (optional)
Standard 14058 contains the following sections:
- Thermal resistance: measures the properties of textile materials and the resistance of a material to the flow of heat between the two sides of the material. It is rated from 1 to 3 with 3 being the highest protection.
- Air permeability (optional): resistance to the passage of air through fabrics. It is scored as 1 or 2, with 2 being the highest protection.
- Resistance to water penetration: resistance to the passage of water through fabrics. It is scored with a 1 or 2, with 2 being the maximum protection.
- Effective thermal insulation (optional): static dummy test.
- Resulting effective thermal insulation (optional): test carried out on a mannequin with arms and legs in motion.
EN ISO 11611
Welding and related activities
Protection against splashes, short flame contact and radiant heat from the electric arc. Minimises the risk of electric shock from contact with conductive materials.

- Class 1
Protection against less hazardous welding techniques and situations resulting in lower levels of molten metal spatter and radiant heat. - Class 2
Protection against more hazardous welding techniques and situations that produce higher levels of molten metal spatter and radiant heat.
For this standard, different tests are carried out and depending on the result, the garment is categorised as Class 1 or Class 2, the latter being the highest.
The tests are:
- Class 1: radiation heat transfer of 7 seconds and splashing of 15 drops of molten metal.
- Class 2: 16 seconds radiant heat transfer and splashing of 25 drops of molten metal.
EN 343
Rain
Protection in environments characterised by the possible combination of these conditions: rain, fog, ground humidity and wind at temperatures as low as -5°C.

- X Resistance to water penetration
- Y Resistance to water vapour <br> Full Garment Test
In it we can find 3 measured categories:
- Resistance to water penetration: resistance to the passage of water through the fabric and tested on material and seams.
- Water vapour resistance: resistance to the passage of water vapour through the garment.
- Full garment test: rain effects tested from above.
The first two are scored from 1 to 3, with 3 being the highest protection. On the other hand, an X or an R marks whether or not the third category has been achieved.
EN ISO 11612
Heat and flame
Protection against exposure to radiant, convective or contact heat and molten metal splashes.
Limited flame spread.

- A1/A2 Test method for flame spread
- B Convective heat (1-3)
- C Radiant heat (1-4)
- D Molten aluminium splashes (1-3)
- E Cast iron splashes (1-3)
- F Contact heat (1-3)
EN ISO 20471
High Visibility
Visibility of the user under daylight and/or under headlamp illumination in the dark (in high-risk situations).

- X Class according to material surface and level of visibility
This standard is categorised into classes (1, 2 or 3) according to the surface area of materials and the level of visibility of the garment, the characteristics of which are as follows:
- Class 1: minimum level of protection required.
According to the standard, workers wearing class 1 garments must be able to be fully seen by drivers of vehicles and machinery in situations where these vehicles do not travel faster than 30 km/h. The type of workers who need to wear these class 1 garments are for example workers exposed to traffic in warehouses and car parks. - Class 2: aims to ensure that the worker can be fully seen in adverse weather conditions and in workplaces where machinery or vehicles are travelling at more than 40 km/h (up to a total of 60 km/h). This level of High Visibility is more focused on workers working close to traffic.
- Class 3: is required for anyone working in places where vehicles travel at speeds of 60 km/h and above, motorways, dual carriageways or in and around airports.
EN 17353
Improved visibility
Visibility of the user in daylight and/or under headlamp illumination in the dark (in medium risk situations).

- Class B3
- Retroreflective material on torso and extremities.
- Visibility in dark conditions
For this standard there are several different classes:
- Class A: risk of not being seen only in daytime conditions. The garment is only made of fluorescent material.
- Class B: risk of not being seen only in dark conditions. The garment is only made of retroreflective material.
- B1: freely suspended fitting of retro-reflective material
- B2: retroreflective material on extremities
- B3: retroreflective material on torso and/or extremities
- Class AB: risk of not being seen during daytime, dusk and dark conditions. The garment is made of fluorescent, retroreflective and/or combined materials.
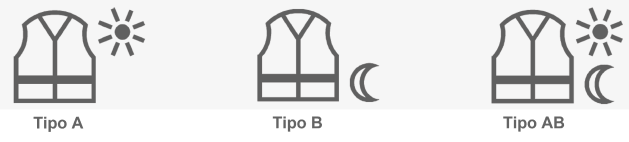
All our enhanced visibility garments are class B level 3 certified.
EN 1149-5
Electrostatic properties
Garments with electrostatic dissipative properties to prevent incendiary discharges.

